The supply situation for the population in the Sahel is dramatic
The earth’s hunger belt means the geographical allocation of an African area in which the population of large parts of neighboring countries is starving. The area extends south of the Sahara across the entire continent from the Atlantic in the west to the Red Sea in the east. This approximately 7000 km long and up to 200 km wide band of the Sahel zone forms the transition from North Africa to Central Africa. The climatic conditions in the Sahel are subject to drastic changes.
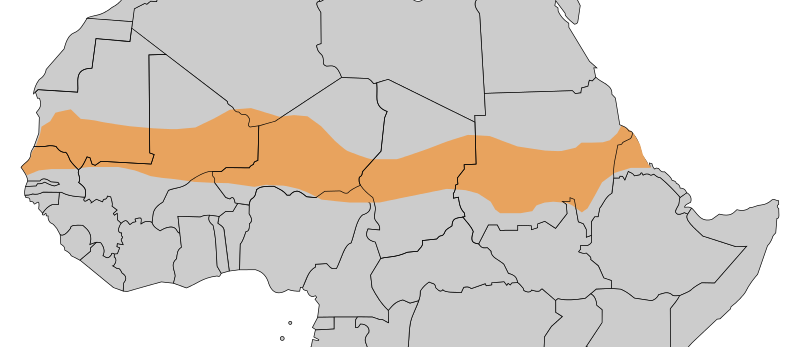 While savannah-typical vegetation develops in the rainy season, drought prevails in the dry season, with most rivers drying up. Since agricultural products to feed the population can only be produced in the rainy season, supply deficits inevitably arise. Due to climatic changes, the dry seasons have lengthened and the droughts widened. In addition to the hoped-for harvests, livestock also fell victim to the drought. This further destabilized the already critical supply situation. The hunger belt includes parts of the following countries:
While savannah-typical vegetation develops in the rainy season, drought prevails in the dry season, with most rivers drying up. Since agricultural products to feed the population can only be produced in the rainy season, supply deficits inevitably arise. Due to climatic changes, the dry seasons have lengthened and the droughts widened. In addition to the hoped-for harvests, livestock also fell victim to the drought. This further destabilized the already critical supply situation. The hunger belt includes parts of the following countries:
- Ethiopia
- Burkina Faso
- Eritrea
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Senegal
- Sudan
- Chad
The plight of the Sahel population has various reasons
The supply problem is exacerbated by several influencing factors. Due to the global economic development, agricultural products from the affected area can hardly be sold for a living. Overproduction of grain in countries outside Africa in particular is depressing market prices. Infrastructure, free trade and security are severely restricted by armed conflicts in some countries.
In addition, this leads to flows of refugees into neighboring countries within the Sahel zone, which cannot be adequately supplied there. The necessary international support is too little and is ineffective due to local distribution problems. In some countries there is a lack of funds for adequate medical care for people who are already weakened by nutrient deficiencies. An estimated 5 million people in the Sahel region need help due to malnutrition, including 1.6 million children.
The supply of potable water is also becoming increasingly difficult. The strong growth in the population exacerbates the supply problem.
Some countries in the Sahel are among the poorest on earth
More drought and wind due to the climatic changes as well as excessive demands on the soil seem to be an insurmountable problem. The nomadic behavior combined with the constant search for vegetation and water is increasing. There is a lack of irrigation systems and storage technologies to prevent the soil from drying out.
Civil war unrest, diseases such as Ebola and the expansion of the desert landscape prevent investments by foreign companies. Security is also undermined by corruption, numerous extremists and aggressive smugglers. This complicates and often prevents the work of aid organizations. International aid funds are often not targeted and insufficient. So it is not surprising that countries in the Sahel are among the poorest in the world.
There are currently first attempts to improve the cultivation options. The planting of resistant trees for the purpose of providing shade and desert-resistant plants are part of it. However, the end of unrest and the formation of stable, democratic governments seem to remain a wish for a long time.
